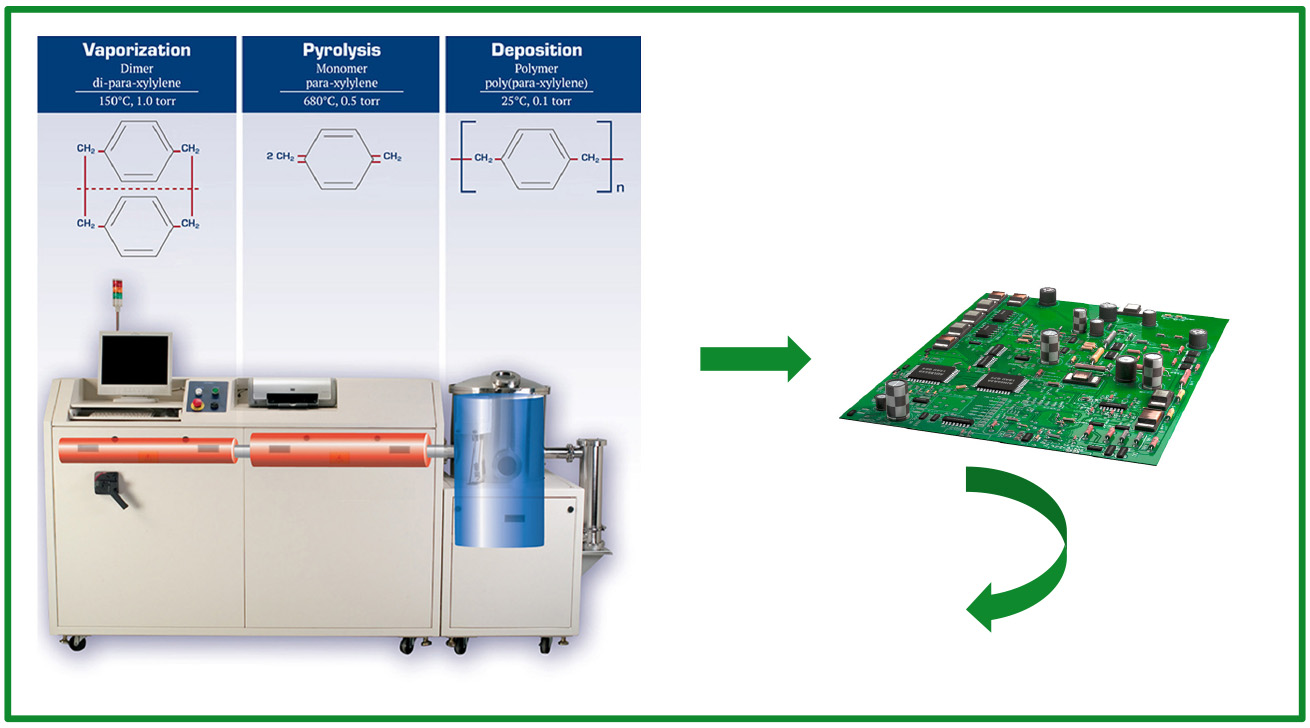
Product Process
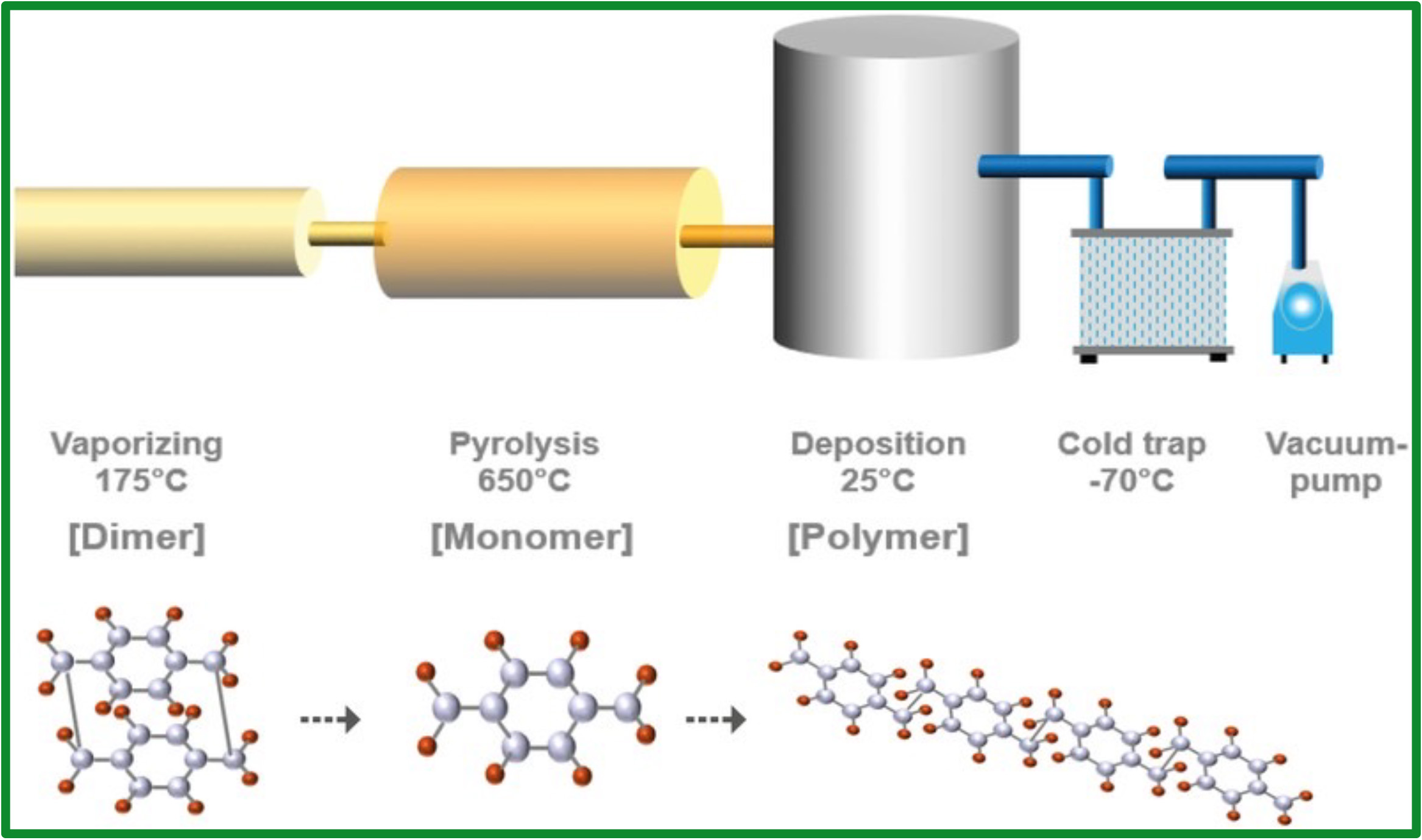
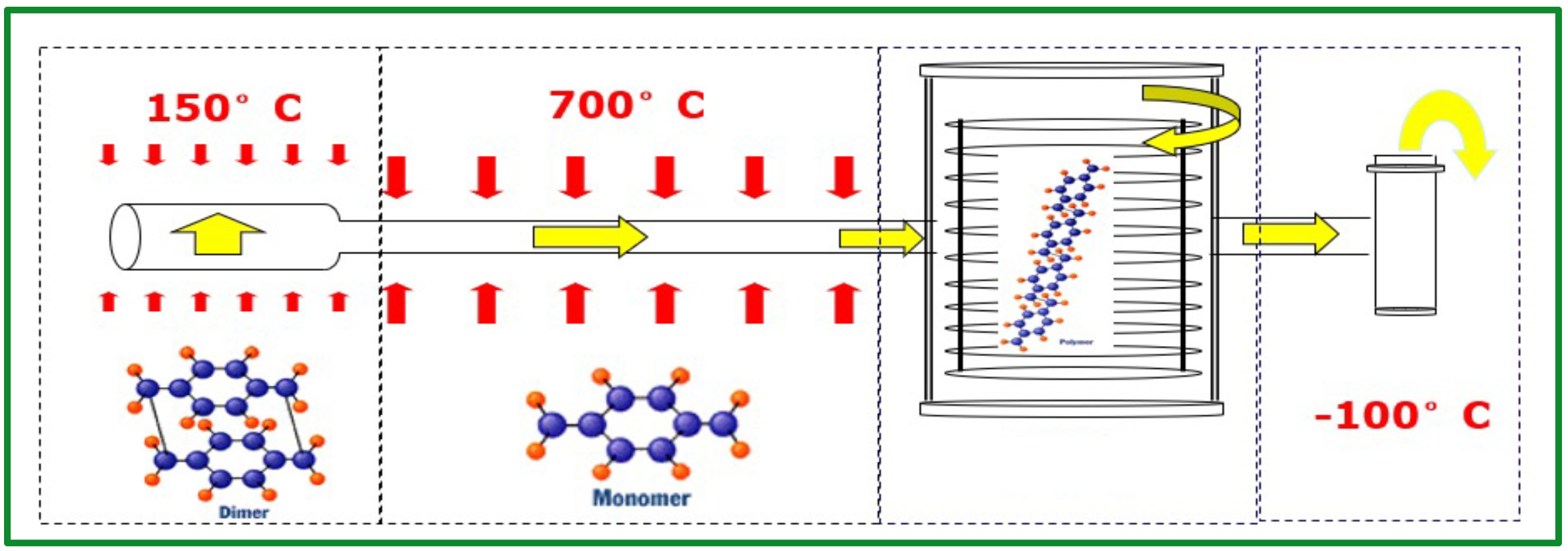
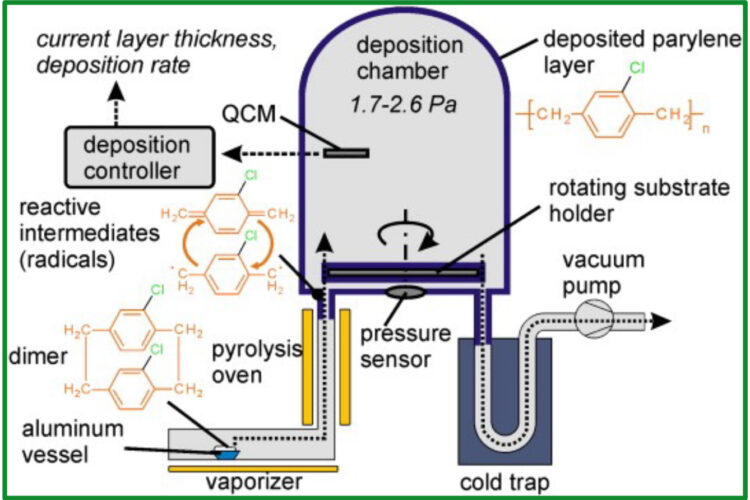
Vaporization Stage
Raw material dimer is vapourised under Controlled temperature Temperature setting depends on amount of dimer used and coating thickness.
Pyrolysis Stage
Gas dimer undergoes pyrolysis under high heat to break down into reactive monomers which then flows into the vacuum chamber.
Deposition Stage
Reactive monomers flows into chamber under high vacuum state and cools to form polymer layer, Necessary for products to be in vacuum and rotated for uniform.
Cold trap Stage
The excess monomer is cooled through the cold trap and dispose Environmentally friendly.
Applied via vapour deposition in a vacuum chamber, the Parylene Coating Process exhibits superior characteristics and addresses shortcomings of traditional coating processes.
- Vapourization of polymer material
- Pyrolysis to Monomer
- Deposition on Surface at room temperature and in vacuum
- No cure forces
- No thermal reactions
- No expansion or contraction
- Very high degree of penetration/conformity
- under, inside, edges and sides
- No liquid phase
- No meniscus, no edge effects
- Nothing to leach out or outgas